In today’s fast-paced world, stress has become a common companion in our daily lives. But have you ever wondered about the profound impact it can have on our overall health? In this blog post, we will delve into the various physiological, cardiovascular, and immune effects of stress, shedding light on the intricate connection between our mental well-being and physical health. Moreover, we will explore the psychological consequences that chronic stress can bring and shed light on the link between stress and mental illness. So, grab a cup of tea, sit back, and join us on this informative journey.
Understanding the Physiological Effects of Stress
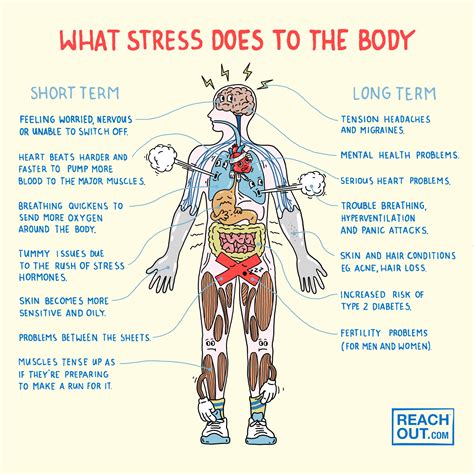
Stress is a natural response to challenging or threatening situations. It can arise from various sources, such as work pressure, relationship problems, or financial concerns. While some stress can be beneficial, chronic or prolonged stress can have detrimental effects on our physical and mental health. In this blog post, we will delve into the physiological effects of stress and explore how it impacts our overall well-being.
When we experience stress, our bodies go through a series of physiological changes. One of the key players in this process is the adrenal gland, which releases stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones trigger the “fight or flight” response, preparing our bodies to either confront the stressor or escape from it. Cortisol, often referred to as the stress hormone, increases glucose levels in the blood and suppresses non-essential bodily functions, such as digestion and reproductive system.
Another notable physiological effect of stress is its impact on the cardiovascular system. When stress hormones are released, they cause our heart rate and blood pressure to rise. This response is essential in emergency situations as it ensures adequate blood flow to our muscles and organs. However, prolonged or chronic stress can put a strain on the cardiovascular system and contribute to the development of heart disease or other cardiovascular conditions.
In addition to the cardiovascular system, stress also affects our immune system. While short-term stress can enhance immune responses, chronic stress can weaken our immune defenses, making us more susceptible to infections and illnesses. The release of stress hormones, like cortisol, can suppress the activity of immune cells, reducing their ability to fight off pathogens effectively.
Understanding the physiological effects of stress is crucial in managing and mitigating its impact on our health. By recognizing the intricate connections between stress and our body’s response, we can implement strategies to promote stress reduction, such as exercise, meditation, and relaxation techniques. Additionally, seeking support from healthcare professionals or mental health experts can also assist in navigating the complex relationship between stress and our well-being.
| Physiological Effects of Stress |
|---|
| Increased release of stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline |
| Raised heart rate and blood pressure |
| Suppression of immune system activity |
| Higher risk of cardiovascular diseases |
In conclusion, stress can have profound physiological effects on our bodies. From hormone release to cardiovascular strain and immune system suppression, chronic stress can play a significant role in the development of various health conditions. By understanding these physiological effects, we can take proactive measures to manage stress and prioritize our well-being.
The Link between Stress and Cardiovascular Health
Stress is something that each and every one of us experiences at some point in our lives. It can stem from various sources such as work, relationships, or even financial struggles. But have you ever wondered about the impact stress has on our cardiovascular health? It turns out that there is a strong link between stress and the well-being of our hearts.
When our bodies perceive a threat or a stressful situation, a physiological response known as the “fight or flight” response is triggered. This response is a natural defense mechanism that prepares our bodies to either confront the threat or run away from it. During this response, there is an increase in the production of stress hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline, which can have detrimental effects on our cardiovascular system.
One of the immediate effects of stress on our cardiovascular health is an increase in heart rate and blood pressure. This is a result of the body’s attempt to pump more blood to the muscles and organs in order to prepare for action. While this response is beneficial in short bursts, chronic or long-term stress can lead to sustained high blood pressure, which can put a strain on the heart and lead to cardiovascular diseases.
Additionally, stress can also affect other risk factors for heart disease such as cholesterol levels. When we are stressed, our bodies tend to produce more LDL cholesterol, also known as the “bad” cholesterol. High levels of LDL cholesterol can lead to the formation of plaques in the arteries, narrowing them and increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
In addition to these physiological effects, stress can also influence behaviors that negatively impact cardiovascular health. People often turn to unhealthy coping mechanisms such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, or overeating when under stress. These behaviors can contribute to the development of cardiovascular diseases and further exacerbate the negative effects of stress on the heart.
To better understand the link between stress and cardiovascular health, researchers have conducted numerous studies. One notable study found that individuals who reported higher levels of stress had a significantly increased risk of developing coronary heart disease. Another study demonstrated that chronic stress can lead to inflammation, a key factor in the development of atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular diseases.
In conclusion, it is clear that stress and cardiovascular health are closely intertwined. The physiological effects of stress, such as increased heart rate and blood pressure, combined with unhealthy coping behaviors, can have a detrimental impact on our hearts. It is important to recognize and manage stress in order to protect our cardiovascular well-being. Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as exercise, mindfulness, and seeking social support can all contribute to a healthier heart. By taking proactive steps to reduce stress, we can ultimately improve our overall cardiovascular health and lead a happier, healthier life.
How Stress Impacts Our Immune System
Stress is a common occurrence in our daily lives, affecting our physical and mental well-being in various ways. One aspect of our health that is particularly vulnerable to the negative effects of stress is our immune system. When stress levels become too high or chronic, they can significantly impact the effectiveness of our immune response, making us more susceptible to infections, illnesses, and even chronic diseases.
One of the primary ways in which stress impacts our immune system is by suppressing its function. When we experience stress, our body releases stress hormones, such as cortisol, which can impair the ability of immune cells to carry out their functions properly. This suppression of immune function can leave us vulnerable to infections and decrease our ability to fight off diseases.
Furthermore, chronic stress can also lead to inflammation in the body, which is closely linked to immune system dysfunction. When we are under constant stress, our body’s inflammatory response can become overactive, leading to chronic inflammation. This chronic inflammation can then contribute to the development of various conditions, including autoimmune disorders and other chronic illnesses.
In addition to suppressing immune function and promoting inflammation, stress can also impact the production of immune cells. High levels of stress can disrupt the balance of immune cells in our body, leading to an overproduction of certain cells while suppressing the production of others. This imbalance can compromise the overall effectiveness and efficiency of our immune system, making us more susceptible to infections and diseases.
To combat the negative impact of stress on our immune system, it is crucial to practice effective stress management techniques. This may include regular exercise, getting enough sleep, practicing relaxation techniques such as meditation or deep breathing, and seeking support from loved ones or professionals. By reducing stress levels and promoting overall well-being, we can help support a healthier immune system and reduce the risk of immune-related health issues.
Key Points:
- Stress can suppress immune function, leaving us more susceptible to infections and diseases.
- Chronic stress can lead to inflammation, contributing to the development of chronic illnesses.
- Stress can disrupt the production and balance of immune cells, compromising the effectiveness of our immune system.
- Practicing effective stress management techniques is essential to support a healthy immune system.
Table: Effects of Stress on the Immune System
| Effects | Consequences |
|---|---|
| Suppression of immune function | Increased vulnerability to infections |
| Promotion of chronic inflammation | Contribution to chronic illnesses |
| Disruption of immune cell production and balance | Compromised immune response and increased risk of diseases |
Overall, understanding how stress impacts our immune system is crucial for maintaining optimal health. By recognizing the connection between stress and immune function, we can take proactive steps to manage stress and support our immune system’s ability to protect and defend our body. Remember, taking care of our mental and emotional well-being is just as important as taking care of our physical health.
Exploring the Psychological Consequences of Chronic Stress
Chronic stress is a pervasive issue in today’s fast-paced society. The constant pressures and demands we face can take a toll on our mental and emotional well-being. In this blog post, we will delve into the psychological consequences of chronic stress and explore how it affects our overall quality of life.
One of the most significant psychological consequences of chronic stress is the development of anxiety and depression. When we are constantly under stress, our bodies release stress hormones such as cortisol, which can disrupt the balance of neurotransmitters in our brains. As a result, we may experience feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and worry. Anxiety disorders and depression often go hand in hand with chronic stress, and they can have a profound impact on our ability to function in our daily lives.
In addition to anxiety and depression, chronic stress can also lead to cognitive difficulties. Research has shown that chronic stress can impair our ability to concentrate, make decisions, and remember information. This is because prolonged stress can actually shrink the hippocampus, a region of the brain responsible for memory and learning. These cognitive impairments can further exacerbate stress levels, creating a vicious cycle of decreased cognitive function and increased stress.
- Decreased productivity: Chronic stress can make it challenging to stay focused and motivated, leading to decreased productivity in various aspects of life such as work or school.
- Sleep disturbances: Many individuals with chronic stress experience difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, which can further contribute to fatigue and overall decline in mental well-being.
| Psychological Consequence | Description |
|---|---|
| Anxiety and Depression | Feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and excessive worry. |
| Cognitive Difficulties | Impaired ability to concentrate, make decisions, and remember information. |
| Decreased Productivity | Difficulty staying focused and motivated, leading to decreased productivity. |
| Sleep Disturbances | Difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, contributing to fatigue and decline in mental well-being. |
It is important to recognize the psychological consequences of chronic stress and take steps to manage and reduce it. Effective stress management techniques such as engaging in regular exercise, practicing mindfulness and relaxation techniques, and seeking support from loved ones or professionals can make a significant difference in our mental well-being. By addressing the connection between chronic stress and its psychological consequences, we can work towards leading healthier, happier lives.
Addressing the Connection between Stress and Mental Illness
Stress is a prevalent issue in today’s fast-paced society, and its impact on our mental health cannot be undermined. Research has shown a clear connection between stress and the development of mental illnesses such as anxiety disorders, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Understanding and addressing this connection is crucial for both individuals and healthcare professionals in order to effectively manage and treat these conditions.
One of the key ways in which stress contributes to mental illness is through the disruption of the body’s stress response system. When we experience stress, our body releases stress hormones such as cortisol, which can have detrimental effects on the brain if chronically elevated. Prolonged exposure to high levels of stress hormones can lead to structural and functional changes in the brain, particularly in areas responsible for regulating emotions and mood.
In addition to the physiological impact, stress also influences our thoughts, emotions, and behaviors, making individuals more vulnerable to developing mental health disorders. Constant worry, racing thoughts, and increased irritability are common symptoms of stress that can contribute to the development of anxiety disorders. Moreover, the negative impact of stress on sleep patterns and appetite can further exacerbate mental health issues.
- Chronic stress can impair our ability to cope with daily challenges and increase the risk of developing depression.
- Studies have shown a strong association between stressful life events and the onset of PTSD.
- Individuals with pre-existing mental health conditions may be more susceptible to the adverse effects of stress, as their coping mechanisms and resilience may already be compromised.
| Effects of Stress on Mental Health: | Common Mental Health Disorders Associated with Stress: |
|---|---|
| Increased risk of anxiety disorders | Anxiety disorders (e.g., generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder) |
| Elevated likelihood of developing depression | Depressive disorders (e.g., major depressive disorder) |
| Potential for the onset of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) | Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) |
To address the connection between stress and mental illness, it is essential to focus on effective stress management techniques and prioritize self-care. Engaging in regular exercise, practicing relaxation techniques (such as deep breathing and meditation), maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and seeking social support are all important strategies to mitigate the impact of stress on mental health.
Furthermore, seeking professional help from therapists or counselors trained in stress management and mental health can provide valuable guidance and support. These professionals can help individuals develop healthy coping mechanisms, identify and challenge negative thought patterns, and provide evidence-based treatments for managing stress-related mental health conditions.
Addressing the connection between stress and mental illness requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses both individual efforts and societal changes. By recognizing the impact of stress on mental health and taking proactive steps to manage stress effectively, it is possible to mitigate the development and progression of mental illnesses associated with stress.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question: What are the physiological effects of stress?
Answer: Stress can have various effects on the body, including increased heart rate, elevated blood pressure, shallow breathing, muscle tension, and increased levels of stress hormones like cortisol.
Question: How does stress impact cardiovascular health?
Answer: Chronic stress has been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, such as heart attacks and strokes. Stress can contribute to the development of hypertension, atherosclerosis, and can negatively affect heart health.
Question: How does stress affect our immune system?
Answer: Stress can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections, illnesses, and diseases. Prolonged stress can impair the immune response, leading to reduced immunity and slower healing.
Question: What are the psychological consequences of chronic stress?
Answer: Chronic stress can lead to various psychological issues, including anxiety disorders, depression, irritability, mood swings, insomnia, and difficulty concentrating. It can also exacerbate existing mental health conditions.
Question: Is there a connection between stress and mental illness?
Answer: Yes, there is a clear link between stress and mental illness. Chronic stress can increase the risk of developing mental health disorders, such as anxiety disorders, depression, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and even schizophrenia.
Question: How can stress be addressed to reduce its impact on mental health?
Answer: To address the connection between stress and mental illness, it is important to practice stress management techniques, such as exercise, mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, seeking social support, and engaging in activities that promote relaxation and self-care.
Question: How can one reduce stress levels for better overall well-being?
Answer: Some effective ways to reduce stress include engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, practicing relaxation techniques like yoga or tai chi, seeking therapy or counseling, and establishing a good work-life balance.